The seizures started for the first time with a frightened expression in my then 4 year old precious daughter’s eyes, and I thought she had seen a ghost. She held her chest, looked wide eyed, ran over to me and buried her head into my stomach where I felt her heart beating hard and fast. It lasted a few seconds and then I reassured her and on went on. She said it was like strong butterflies in her belly. It also was the morning after her lovely grandparents left after a 3-month visit back to Ireland and we were all very sad.
For approximately one year prior to this, she had been complaining of stomach aches, top and bottom, occasionally under her ribs. She had reduced appetite and a very worrying paleness. She also was very car-sick so we had to prepare for longer journeys. I had been to the ER after Christmas lunch when she had terrible stomach pain. She was checked to be ‘fine’ but I was advised to see a pediatrician to follow up.
Panic Attacks or Seizures?
Basic blood tests confirmed she was in ‘great health’, with the only thing they found in a stool test being h-pylori. So it was their opinion that she wasn’t having seizures but instead must be anxiety/panic attacks as she is a sensitive child. I was always skeptical, but in absence of any other data, we waited a long time for the referred psychologist. After 3 sessions, I realized they had no intel and were chasing the wrong dragon. I kept saying she looked somewhat unwell. The seizures were happening quite infrequently then, perhaps one episode a month, or every 2-3 weeks, but then when she started kindergarten they ramped up a little more frequently. She would stop, look to be catching her breath, hand twisting for a few seconds and then it was over. I thought it was a reaction to the food they fed her there that we didn’t have at home, or a recent childhood vaccination or that she hated being away from me there. I also noticed she reacted with bad behavior and potential episodes after certain foods- e.g. ice cream especially and any food dyes/flavors. So our already healthy diet went up a notch to exclude these. I also did gluten and dairy free on advice from naturopaths. It was strict and sad.
Then these episodes changed to resemble a seizure more directly, not a panic attack. I got rid of the useless pediatrician who was actively gaslighting me to try to minimize the symptoms or their own incompetence and I demanded to see a neurologist. It was again a very long waiting game. When the day came, we were very nervous but were looking forward to some potential answers. He was a neurologist at a prominent Children’s Hospital, so I had high expectations. I still had many questions and areas to workshop but after he ran through my extensive notes and a video I took, he said ”let me stop you, She has epilepsy and ‘NOTHING YOU DO WILL EVER MAKE A DIFFERENCE. She will need medication for life and if that fails an operation”. This was also via video link, as it was during a Covid lockdown. No physical examination and a script sent in the mail. I accepted these, as I know you don’t refuse unless you want trouble, but my intention was to never band-aid or experiment, especially not with a young child and my family’s history of sensitivity to medication. Thank god he lied so blatantly when he said ”there’s no side effects from the anti-seizure meds” to know we weren’t dealing with the truth or someone who could be trusted.
We did another two MRIs, but they were clear. They wanted a third with dye contrast but I refused that and as I learned more about her case, know why I felt so strongly about that.
A Parade of Doctors
We embarked on the alternative/functional medicine pathway, as that is something I am familiar with. I didn’t realize how challenging it was going to be. We went from one to the other. I was constantly seeking experts who possibly knew more than the last. I needed help to decode this horror. I know a healthy child doesn’t get a whisper of issues that then progress to a scream over years for no reason.
With each new practitioner, we did another test. This included blood tests, stool test, hair tests, OAT test, Pyrrole and extensive Genetic testing. She was found to have higher copper ceruloplasmin to be treated simply with zinc, which was always met with a seizure so we stopped that. She had high vitamin D and B12, but another test found that potentially wasn’t a true representation. It can be in the blood reading but not necessarily in her cell. This is where you really throw your hands-up and say what chance do we have if some test results can also be falsely represented!!!!!
The genetic testing provided the best clue that we weren’t dealing with an easy case- she had heterozygous compound MTHFR, and many other compromising genes that are not ideal on many pathways, especially detox. This also got me remembering how I haven’t felt optimal for years. I put it down to extreme stress with my daughter. A huge thing I always wanted to understand was why I was so incredibly sick with Hyperemesis Gravidarum the entire pregnancy with her. I have always believed this had to have impacted her somewhere but could never nail down a connection.
After 5 naturopaths and numerous consults from other medical professionals, listening to one bogus diet restriction after the next, many different versions of expensive supplements that basically all triggered her. Nothing was working. She was having seizures weekly or more particularly is she was sick or overly stressed. The closest theory I could deduce of was a type of MCAS or histamine intolerance and the symptoms were:
- Crying out prior
- Frequently occurring in sleep waking her bolt upright
- Hyperventilation/can’t get air
- Big scared eyes
- Drooling, disorientated
- Body shaking, head was twisting hard to the side like dystonia, arms curled, torso completely contorted.
This would last for about 30 sec-1 min. The horror of witnessing this is imprinted on my soul forever. She began to lose balance so we would have to grab and hold her and I would blow hard in her face to try to get it to finish. It started to become dangerous if we weren’t around to catch her.
I also simultaneously worked back one item at a time to try to fix every variable I could, including environmental. There was a mold spot in our house in the room she slept in the bathroom. It took a long time to get repaired, I pondered about that exposure and if the builder actually fixed the leak properly. Our awful neighbor had smoky barbeques numerous times a week on the fence-line using building offcut wood. The smoke permeated our house. We sold our house to see if that made a difference and moved to the country with my parents’ house in the green clean air.
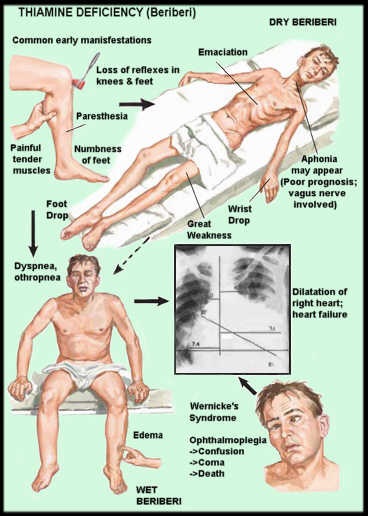
Thiamine and Riboflavin Deficiencies With Genetic Underpinnings
I finally found a practitioner trained in epigenetics with a naturopath background as I wanted someone like Ben Lynch. His YouTube videos were the only things that made sense to break down a complex health issue. She was a blessing and truly eclipsed the level of detail of knowledge (and empathy) by all others. She looked at the OAT test (shown to 5 people previously) and saw immediately she had very high lactic acid and some other markers indicating thiamine deficiency, critically followed by a riboflavin (B2) deficiency. She advised to not give a B complex and work through one at a time.
When we tried to treat this with thiamine and a B2 capsule. I am sure she had a paradoxical reaction as she had 8 seizures in the night. It was horrifying. I wanted to abort this plan like so many other failed attempts, as I never prolong anything that’s not showing positive traction, but something told me to break it down and do one step at a time. I went back into her genetics myself and looked at the thiamine related genes. She had homozygous defects in a key thiamine transporter (SLC19A2) and an enzyme (thiamine pyrophosphokinase – TPK1) that turns free thiamine into its bioactive form thiamine pyrophosphate. She also had SNPs in several other key thiamine genes, in addition to SNPs in several other mitochondrial genes.
I also came across and watched Elliot Overton’s Thiamine videos on YouTube and how to correctly dose-up. I also read many insightful articles on the Hormones Matter website. I tried again with low dose of b1 (about 5mg), some magnesium and potassium-coconut water. The seizures, in the midst of a horrible flare, stopped immediately and didn’t return for over 2 months. I dosed twice a day and worked up to 50mg of thiamine in total, which is where she is currently. She also got much better color in her face. It truly felt like a miracle!
What Else Are We Missing?
The miracle, however, ended and the seizures have been creeping back in and I’m not sure why. They seem not quite as severe in presentation, however they still occur about once a week to every 2 weeks. I need to understand why and how to help her as my intuition screams at me to find the answer, and quick! She is now 8 years old and I am struggling to comprehend any more of her childhood being stolen.
We Need Your Help
More people than ever are reading Hormones Matter, a testament to the need for independent voices in health and medicine. We are not funded and accept limited advertising. Unlike many health sites, we don’t force you to purchase a subscription. We believe health information should be open to all. If you read Hormones Matter, and like it, please help support it. Contribute now.
Yes, I would like to support Hormones Matter.
Photo by Noah Silliman on Unsplash
This article was published originally on September 11, 2023.