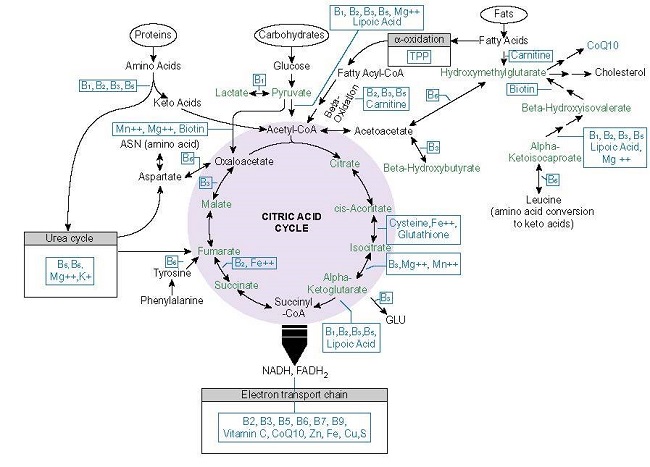
Much of our understanding regarding thiamine deficiency comes from early reports of illness from far-off lands, case reports that suggest rarity, and from rodent studies. While all of these are useful, none easily translate to the realities of this disease process on the ground, in the clinician’s office, or in the hospital. Do we really know what thiamine deficiency, or more appropriately, thiamine insufficiency looks like in everyday practice? Would we recognize it in the patients who walk through the doors of any medical facility? Probably not. And that is a problem.
We tend to think about nutrient deficiencies as emerging only in populations affected by starvation or absence-based malnutrition. This interpretation evolved from the early descriptions of beriberi, where the individuals most afflicted included Japanese sailors, Pacific Island communities, and regions afflicted by food scarcity. Later, alcoholics were added to the list of potential populations affected by thiamine deficiency. More recently, post gastric bypass patients, hyper-emetic pregnant women, and patients with critical illnesses were identified as at risk for deficiency. With each set of populations though, we are given the impression that thiamine deficiency is rare but easily recognized. It is neither, but the lens through which we view this disease process was focused generations ago on only the most severe examples, and that lens has remained ever since.
The Legacy of Early Scientists
The typical descriptions of thiamine deficiency disease, come from the perspective of the early investigators who described these conditions and have changed very little in decades since. Definitions of beriberi, which in Japanese means I cannot, I cannot, was, and still is, largely focused on the progression to heart failure in later stage deficiency. Here, there are two primary types of beriberi: wet beriberi, which is defined as high output cardiac failure with edema, and dry beriberi described as the central and peripheral nervous system and cardiovascular disturbances without edema. In recent years, gastrointestinal beriberi and neuritic beriberi have been added but they remain poorly recognized.
Likewise, our understanding of Wernicke’s encephalopathy (WE), a disease process that was first described by Carl Wernicke in 1881 and later associated with alcoholism and thiamine deficiency, is still described using Wernicke’s original triad of symptoms: mental confusion, ocular abnormalities, and ataxia. This despite the fact that 1) these symptoms represent a later stage manifestation of the disease process, where the deficiency is sufficient to produce brain damage and 2) these symptoms infrequently present, either alone or in combination, in most cases of WE. In fact, one study found that 80% of cases WE were identified only postmortem, meaning they were missed entirely while the patient was alive. Of those, only 16% had documentation of all three symptoms, 44% had one or two of the classic triad symptoms and 19% had none at all. This suggests that the classic triad, while a brilliant original observation, requires adjustment.
Korsakoff’s syndrome, a later stage and more severe form of thiamine deficient brain damage that includes neuropsychiatric and neurocognitive manifestations like confabulation, psychosis, and significant memory deficits, shares a similar lack of diagnostic clarity and is often mistaken for more traditionally defined psychiatric cases and dementias. Like Wernicke’s syndrome, Korsakoff’s is named after the scientist who first reported it in the late 19th century, a Russian by the name of Sergei Korsakoff. Like Wernicke’s, the lens through which we view this disorder owes largely to the original descriptions. Both syndromes are now combined as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (WKS). For that reason, there are no clear data on the prevalence of Korsakoff’s syndrome or on how many patients progress through the different stages of brain damage associated with thiamine deficiency.
Those Rare Cases of Thiamine Deficiency
Modern case reports reinforce these legacy definitions of thiamine disease and continue to portray thiamine deficiency as a rare manifestation of severe illness. The literature is replete with cases of patients who demonstrate none of the classic symptoms associated with thiamine deficiency and yet are clearly deficient. Likewise, in each of these reports, the development of thiamine deficiency is considered rare. Indeed, the rareness of this condition is almost always explicitly emphasized in the text with statements like:
- “A severe depletion is not commonly seen, except in cases of inadequate nutrition and/or alcoholism.”
- “Cardiac beriberi, or heart failure due to thiamine deficiency, is considered rare in the developed world.”
- Thiamine deficiency is rare in developed countries and is most commonly associated with chronic alcoholism. The other predisposing conditions include chronic dietary deprivation and impaired absorption or intake of dietary nutrients.
- Nowadays, in the developed world it is relatively rare.
Next time you are reading a case study, or really, any report on thiamine deficiency, note the remarks of rarity. What if thiamine deficiency is not rare, but simply under-recognized? If we rarely consider it based on the lack of matching symptoms, how do we know what the real prevalence is?
Of Rodents and Men
The rodent research, although more adept at addressing the progression of deficiency symptoms across time, is still problematic. Aside from the obvious differences between rodents and humans, the highly controlled and contrived experimental conditions under which this research occurs in no way reflects the messiness of life. Rarely are we exposed to an absolute deprivation of a single nutrient, unless under some sort of duress or a medical error. More frequently, the progression to thiamine deficiency is an extended process of months to decades, where exposure to thiamine or anti-thiamine factors varies across time, and as a result, so too does the expression of illness.
From the rodent research, we do know, however, that there is a clear progression of symptoms across the period of deprivation. Here, among the first manifestations of thiamine deficiency are hair loss, apathy, and anorexia. These symptoms emerge within two weeks of thiamine deprivation. At about 4 weeks, neurological symptoms emerge, and death by cardiac arrest occurs at about 6 weeks.
Whatever the problems there are translating patterns gathered from animal research to those of human studies, and there are many, at least with these studies we can see the early indicators of problems. If a patient were to complain of new-onset hair loss, apathy, or anorexia, or even newly emerging neurological symptoms, more often than not, the symptoms would be dismissed as stress-related and relegated to the category of psychosomatically induced. An antidepressant or anxiolytic would be prescribed and that would be the end of it. Thiamine or other nutrient deficiencies would not be considered until a much later stage, if at all.
The Progression of Symptoms in Human Females
From some highly unethical studies conducted on female psychiatric patients in the late 1930s and early 1940s, we know that the human progression of thiamine deficiency does indeed mirror what is illustrated by animal research somewhat. The early symptoms are so benign that most would miss them. Similarly, as the symptoms build over time, although they worsen considerably, they remain more general than specific and might easily be ascribed to other conditions if one were not trained to consider thiamine.
A few notes about the studies. There were three in total, two with four women each and one with 11 women maintained on a diet of .15mg of thiamine per day for 147 days, .45mg of thiamine for 88 days, and 11 women at ~.15 – .2mg thiamine per day plus 1mg of thiamine given intermittently for up to 196 days, respectively. In the third study, where additional thiamine was provided, when averaged, the total thiamine consumed was ~.175mg per 1000 calories of food or .35mg for a 2000 calorie per day diet. Also, in this study, 5 of the 11 women were maintained on the diet for an undisclosed period before resuming a normal diet, while the remaining 6 were kept on the diet for as long as 196 days. This is approximately 30% of the recommended daily allowance needed to stave off deficiency symptoms and syndromes.
Before each study period, the women were provided a normal ‘healthy’ diet for up to 52 days. It is not clear what that constituted. Upon beginning the study, the diets became quite unhealthy, consisting of food products using white flour, sugar, tapioca, corn starch, polished rice, raisins, egg white, cottage cheese, American cream cheese, butter, hydrogenated fat, tea, and cocoa. Additional B vitamins, as well as some fat-soluble vitamins, were provided via supplement, even though thiamine was all but eliminated.
Below is a compilation of the observed symptoms in two of the case descriptions provided.
- First few weeks: emotional instability, irritability, moodiness, anxiety, agitation, depression, reduced activity, and numerous, often vague, somatic complaints. Weakness and anorexia begin to present.
- 30 days: anorexia, weight loss, epigastric distress, increasing weakness, periodic vomiting
- 50 days: nausea and vomiting after meals, progressive weakness from low energy to bedridden, sometimes constipation
- 70 days: constant nausea, severe weakness, apathy, confusion, numbness, and tingling in extremities
- 90 days: inability to read or focus, aberrant to absent sensory recognition, tender calves, inability to stand from squatting position, hypoactive Achilles tendon reflex, nausea continues progressing to regular vomiting after meals
- 110 days: appetite fails, apathy, vagueness and confusion, low blood pressure and heart rate at rest, rapid increase upon ordinary exertion, aberrant and absent sensory perceptions, aberrant and reduced reflexes, reduced flexion of ankles and knees, ataxia, inability to stand on toes.
- 120 days: impaired pain perception on legs, loss of patellar and Achilles reflex, weakness in abduction, adduction, and flexion of thighs, weakness in the legs with limited ability to extend legs with quadriceps, inability to stand or walk without support, ankle and knee clonus absent, Babinski response absent.
One of these two subjects developed severe neurological defects at 120 days and so the experiment was stopped. The researchers noted that appetite had completely failed and remarked that ‘inanition seemed imminent. They also remarked that with 60-80mg of thiamine given orally and parenterally many, but not all, of the deficits. Appetite returned and strength was regained within the first week, and within 30 days, the less severely ill of the two women was mostly recovered. At 60 days, she was fully recovered. For the other women, recovery was incomplete, even after 120 days of treatment. Of note, it was the younger and more active woman who suffered the most serious neurological deficits and who was unable to fully recover.
In the 88-day study, the most common and debilitating symptoms included vomiting and subsequent anorexia. The authors note:
We nevertheless are impressed by the degree of debility induced by the isolated withdrawal of thiamine. Fatigue, lassitude, and loss of interest in food developed early and increased progressively as the period of deficiency extended, to the point of intolerance for food. So great was this intolerance that uncontrollable vomiting, even after tube feeding and parenteral injection of solutions of sodium chloride and dextrose, automatically brought the observations to a close.
Also observed in this study, was an association between pre-deficiency energy levels and severity of illness propagated by the deficiency.
The time of development of symptoms and the time of development of severe symptoms differed among the subjects and seemed to be related to physical activity. The subjects who were more active showed symptoms earlier and were more seriously affected later than others who from the beginning were less energetic.
A few additional observations:
- When thiamine was added intermittently, even though the total levels were still considerably below normal, symptoms improved for a period of a few days to a week. This happened repeatedly. The improvement was so noticeable that some of the women begged to remain on the higher levels of thiamine.
- Pyruvate and lactic acid levels were higher throughout the period of thiamine deprivation but peaked differentially by individual, by duration of thiamine deficit, and across time, relative to when dextrose was given.
- Pyruvate and lactic acid levels increased variably after meals and when dextrose was given but returned to the pre-meal/pre-dextrose basal rate within 120 minutes.
Finally, the most notable symptoms in each of the studies involved gastric distress, with vomiting, severe constipation, severe food intolerance, and anorexia. This, of course, was in addition to a decline in energy, polyneuropathy, changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and rhythm, and a decline in cognitive capacity.
So What Does Thiamine Deficiency Look Like?
Everything. And nothing. It is non-specific. It is the sickness behaviors of which Selye writes that underlie all illnesses. Thiamine deficiency looks like every other non-specific illness until it becomes severe enough to approximate some of the more well-recognized aspects of beriberi or WKS. Even in its most severe stages, however, the symptoms could easily be ascribed to other types of illness. Making matters more difficult, unlike the research presented above where thiamine is restricted consistently across time, in modern, developed countries, thiamine is rarely restricted so consistently. Thiamine consumption waxes and wanes across time, as does the demand. It is that mismatch between consumption or availability and needs that initiates the molecular events, deep in the mitochondria where thiamine is critical, that is responsible for the bevy of symptoms attributable to thiamine deficiency. This means that if we rely on the conventional diagnostic parameters, defined generations ago, we are all but guaranteed to miss it. Instead, we ought to be considering thiamine and other nutrient deficiencies in all cases of illness, whatever their manifestation, but that demands an entirely new lens through which to view health and disease; a lens that is quite at odds with the current model of medicine.
We Need Your Help
More people than ever are reading Hormones Matter, a testament to the need for independent voices in health and medicine. We are not funded and accept limited advertising. Unlike many health sites, we don’t force you to purchase a subscription. We believe health information should be open to all. If you read Hormones Matter, and like it, please help support it. Contribute now.
Yes, I would like to support Hormones Matter.
This article was published originally on April 29, 2021.
Photo by Agence Olloweb on Unsplash.