The Perils of Academic Publishing
I am an avid student of cardiology since migraine, my field of interest, is connected to electrolyte imbalance, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system, blood pressure problems, and metabolic disorders, all of which collectively fall into the bucket of SyndromeX. SyndromeX is the disease researchers of the world have been trying to prevent and/or cure—or at least treat successfully—from the middle of the 20th Century through today and likely to continue for the next several decades. Why so long? There seems to be three trends in academic research:
- Poor study design and analyses often compromised by financial interests.
- Only incremental findings are published.
- Paradigm shifting research is rarely, if ever published.
Researchers who cannot publish often say the most important things.
These researchers are shifting the paradigm. When research goes against the current dogma, academic journal editors and reviewers have little interest in publishing. In these fields, particularly in the field of nutrition, researchers can lose their careers, face lawsuits and worse, when they dare to attempt to publish their work (see this page where I quickly saved a publication before it was removed–it is in PDF form) or here where a doctor (not a nutritionist) advised his patients on how to reverse metabolic syndrome by a new diet or here where one of the most famous researchers in the field of nutrition is sued by the same organization (Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA)). By contrast, those researchers who stand on false dogmatic premise always get published because their findings support the findings of the editors, reviewers, and the dominant industry (see here for or here for two sample articles that stand on completely erroneous research but support the dogma; and there are thousands more like these). An example of an historical review of the nutrition industry and how they misled us for over 60 years is published by the British Medical Journal here but it was not without an attack by (I counted) 199 academicians from the school of “Dogma” that demanded the article to be retracted by the journal. You can find their retraction demand here. Some of the signatories–if you are familiar with the nutrition war–will be familiar to you. Luckily the article was not retracted only one sentence was corrected. Another exception that published just two days ago is here. I have yet to see the comments and if it will stay published.
Historically, this has been the case too. Einstein, for example, could not publish any of his papers today–all his papers (except one) were published without the peer review process. Without his findings where would we be today? The one paper that went through peer review was not accepted in that journal and he published without peer review elsewhere. Today, a paper published without peer review is considered to be junk and equal to not having published anything at all. On the flip side, a published peer reviewed article in a top journal does not mean the paper is not junk. Published scientific papers are often junk even if published in the top journals.
In my research field of migraines and how increased dietary salt, for example, reduces migraines, I see this all the time. Migraines are preventable by increased sodium and thus research on sodium and health matters. Hundreds of studies show that it is sugar, and not salt, that increases blood pressure–implying safety in increased salt intake. I found no research that showed the effect of salt on blood pressure that discusses the magnitude of the shift by salt, only that there is a minor shift. The magnitude is tiny; only 2-8 systolic point changes are observed, while a normal daily blood pressure variation considers 39 such point changes as normal. Thus, the change of 2-8 points is statistically not significant at all. I submitted a paper stating this to The Lancet and received the message that “it is not a priority.” I published the paper elsewhere. Less than a year from the rejection, a paper was published in The Lancet along on the same subject, except that it contained an unexpected twist. The article tried to cross the dogmatic line of the “less dietary salt is healthier” while presenting findings supporting the notion that more dietary salt is actually better. Let me show you what I mean. Here is a portion of the abstract.
“Increased sodium intake was associated with greater increases in systolic blood pressure in individuals with hypertension (2·08 mm Hg change per g sodium increase) compared with individuals without hypertension (1·22 mm Hg change per g; pinteraction<0·0001). In those individuals with hypertension (6835 events), sodium excretion of 7 g/day or more (7060 [11%] of population with hypertension: hazard ratio [HR] 1·23 [95% CI 1·11–1·37]; p<0·0001) and less than 3 g/day (7006 [11%] of population with hypertension: 1·34 [1·23–1·47]; p<0·0001) were both associated with increased risk compared with sodium excretion of 4–5 g/day (reference 25% of the population with hypertension). In those individuals without hypertension (3021 events), compared with 4–5 g/day (18 508 [27%] of the population without hypertension), higher sodium excretion was not associated with risk of the primary composite outcome (≥7 g/day in 6271 [9%] of the population without hypertension; HR 0·90 [95% CI 0·76–1·08]; p=0·2547), whereas an excretion of less than 3 g/day was associated with a significantly increased risk (7547 [11%] of the population without hypertension; HR 1·26 [95% CI 1·10–1·45]; p=0·0009).” [Note they state they measured sodium all through the abstract but in the article they used these same numbers for salt. Sodium is 40% of salt. Salt is made of sodium chloride, so “7 gr sodium” would thus be equal to 17.5 gr salt, which is not something they measured or mentioned. Thus the abstract is misleading and confused]
Aside from the almost total incomprehensibility of the text, the abstract appears to suggest that less dietary salt intake is better, when in fact, if we translate and read the rest of the article, it indicates the exact opposite, that more salt is better. Here is my translation–replacing sodium with salt where it is due:
“This study found that increased sodium intake was associated with an increases in systolic BP in individuals with hypertension (2.08 mm Hg change per each gram of sodium increase) compared with healthy individuals. In hypertensive individuals, 7-gram salt [2.8 gr sodium] per day or higher amount, or less than 3-gram salt [1.2 gr sodium] a day were both associated with increased heart risk—meaning some heart event, such as a heart attack. Thus, the ideal daily sodium intake for a hypertensive individual has a definite lower end of 1.2 gr sodium and an upper end of 2.8 gr sodium, with the best outcome reached by hypertensive subjects at 4–5 gr salt [1.6 – 2.0 gr sodium] a day, which also did not harm the healthy population. Healthy individuals suffered when they excreted 3 grams salt [1.2 gr sodium] a day. Healthy individuals had a significantly increased risk of a negative heart outcome (heart attack or similar) from 1.2 gr sodium a day and also greater than 7 grams salt [2.8 gr sodium] a day.”
This was a sly move to suggest two things at once. The strategy worked. The article was published. Unfortunately, the evaluation of the data was flawed and since the presentation of said data obfuscated their real findings, the publication became a confused mess. Moreover, subsequent to the article’s publication, hundreds of other articles have referred to it, as if the findings were correct, deepening the damage this badly analyzed study created.
What the Data Actually Demonstrated
In order to fully illustrate the findings in this study (Associations of urinary sodium excretion with cardiovascular events in individuals with and without hypertension: a pooled analysis of data from four studies), I created two charts using their data.
Figure 1. Death rates per sodium change in hypertensive patients
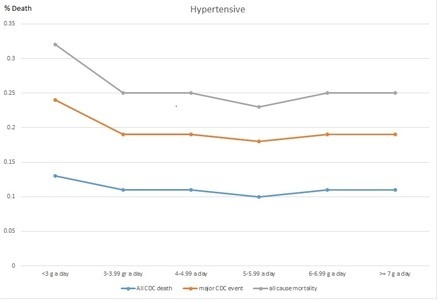
Figure 2. Death rates per sodium change in healthy individuals
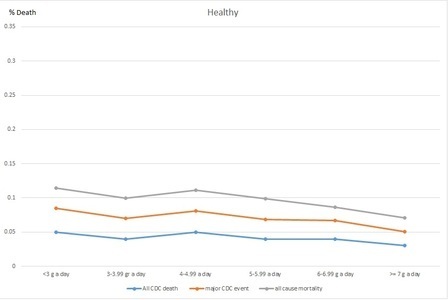
While Figure 1, shows the hypertensive and diabetic patients with a mixed curve-like relation to urinary salt, Figure 2 shows that healthy individuals tend to remain healthier the more salt they have in their urine. The two graphs show that both groups (healthy and hypertensive) tended to die or have cardiac events when less urinary salt was found. Thus, we may conclude that too little urinary salt is unhealthy and that for the healthy, the more salt in the urine the better. Do we know why the unhealthy had low or high urinary salt? No clue. Do we know why the healthy had low or high urinary salt? Nope. Can we conclude anything at all? Yes: in both groups, less urinary salt found in the urine meant earlier death.
The authors of the article did not publish these simple graphs. Why not? Perhaps because these graphs show that the data of the sick and the healthy cannot be combined. Instead, they ran a regression that cancels these differences to some degree, with which the whole article passes on a very confused message. Unfortunately, since The Lancet is the top academic journal, every single medical practitioner, cardiologist, and nutritionist who may gain some insight from an article like this will put it down and head for a walk instead.
These findings could have been important if properly analyzed, since they would represent a paradigm shift in medical understanding of the role of salt in our diet, why the sick are getting sicker and those on low salt diet die faster!
My Take on the Research
The study was flawed from the onset.
- The database they used, PURE, has data from thousands of individuals for general epidemiological analysis and so the control mechanism to conclude any causal relationship is impossible. In particular, reading salt amount in morning fasting urine samples tells nothing about how much salt the individual consumed the day before let alone in general. One cannot conclude a meaningful association between salt amount in urine and salt amount consumed because there are so many factors interfering with the clearance of salt from the body (1-9). Even correlation is dubious; deriving causation is impossible, yet that is precisely what this paper did.
- The authors combined findings of the sick and the healthy, regardless of what heart or diabetic medications the sick were taking (both alter urinary salt content), and created a combined graph representing the recommended daily dietary intake for all people (sick, healthy, children, elderly).
Back to the Perils of Academic Publishing
I wrote a commentary about the flaws and sent it to The Lancet. It was rejected after the editors sat on it for over two months. Why was it rejected? Interestingly, while most academic articles are followed by comments and debates, The Lancet did not allow any comments for or against this particular article. This is odd since without a healthy debate, science heads nowhere. When researchers discover errors or flaws and cannot publish these finding, less discerning readers will continue to misunderstand the research. In this case, most will think that less salt is better for cardiovascular health, when it is absolutely not.
References
- Unger T & Jun Li (2004) The role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in heart failure. Journal of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 5(1 suppl):S7-S10.
- McQuarrie EP, et al. (2014) Association Between Urinary Sodium, Creatinine, Albumin, and Long-Term Survival in Chronic Kidney Disease. Hypertension 64(1):111-117.
- Christensen BM, et al. (2010) Sodium and Potassium Balance Depends on αENaC Expression in Connecting Tubule. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 21(11):1942-1951.
- Ragot S, et al. (2016) Dynamic Changes in Renal Function Are Associated With Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 39(7):1259-1266.
- Mannucci E, et al. (Cardiac safety profile of rosiglitazone. International Journal of Cardiology 143(2):135-140.
- Longo DL, et al. (2013) Harrison’s Manual of Medicine 18th Edition (McGraw Hill Medical, New York).
- DiNicolantonio JJ & Lucan SC (2014) The wrong white crystals: not salt but sugar as aetiological in hypertension and cardiometabolic disease. Open Heart 1(1):e000167.
- Verbalis JG (Disorders of body water homeostasis. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 17(4):471-503.
- Catterall WA (2000) From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron 26.













Interesting article. I am new to academia and research. Not sure if I made a mistake. Has the situation improved at all since you wrote this article?
No Pieter, in fact, it has gotten worse. In fact, just recently this article was published on academia. I copy-paste here the essence of the article:
An influential academic safeguard is distorted by status bias
Sep 14th 2022
I must add that Dr. Vernon Smith, Nobel Laureate of Economics, is a personal friend and was a wonderful colleague when I was teaching at Chapman University. I was very happy to see this wonderful and rather devious public “stunt” revealing how terrible academia and academic publishing actually are. I left academia for this reason in 2008 and have no intention to ever return.
Good luck to you! Since you are new in academia, you may be able to make a difference as well! Try, in any case.
Best wishes,
Angela
Hello!
Have you thought this aroud, from the other view. What happens if a person doesn’t get enougt sodium? His aldosterone goes up to retend sodium to increse the blood pressure and this makes the kidneys to waste potassium into the urine. What do we see in the blood tests? Low potassium and high aldosterone, normal sodium. Blood pressure low, normal or even high depending on how aggressive is the RAA-system response. So, what do we do? Is lowering to sodium intake, increasing potassium intake and eating ACE-blockers really to right answer? Or is it the sodiumchloride, the salt. Is this all indeed because of too low salt intake, boby response to too low blood pressure?
Of course there are diseases that disturds the RAA-system and high hormones without basic reason may lead to high sodium, low potassium and high blood pressure and therefore anything that helps to bring the blood pressure down helps.
But if the reason is from the beginning low blood pressure or sodium depletion, then giving ACE-blockers or betablockers or sodium restriction may even worse the situation.
If you use google scholar, without date limit, and you but there the words “aldosterone migraine” you will get a lot of researches. But if you put there the time limit, let say 2000, you won´t get any. Why? These hormones and salt intake could be the key, so why is it hushed down?
Is it reayly so big tabu to think that more salt could actually be the key?
Dear Susan,
Not sure what you mean. No one is talking about any medicines in the article AND I am talking about a special population whose voltage dependent ionic channels don’t work the same as for other populations plus their RAAS is also modified as a result.
I was not talking about increasing potassium and eating ACE blockers… not sure where you read that. I think you misunderstood the article.
In terms of increase of sodium, please read this article–it is open access. This is just one of many.
Best wishes,
Angela