The term ‘Spin Doctor’ wouldn’t be coined until much later, but it was already clear by the time of the Nelson Pill Hearings that some prominent physicians were willing to twist statistics, incorporate doublespeak, and create confusion in any way they could to defend hormonal birth control. They were Spin Doctors in the truest sense. Fortunately, within the context of Senate Hearings, their ‘spin’ was frequently challenged.
Let the Spin Begin
Dr. Robert Kistner from Harvard couldn’t find a bad thing to say about The Pill if his daughter’s life depended on it. However, simple challenges to his testimony made several of his statements seem comical. Consider this exchange with Ben Gordon from Senator Nelson’s staff, when Dr. Kistner compared pill deaths with those of cigarettes:
Dr. Kistner: For every pill-induced death in Britain there are at least 1,500 cigarette induced deaths; based on the total sales of the two products during 1967 one cigarette is three time as dangerous to life as one pill.
Mr. Gordon: Dr. Kistner, may I interrupt for just one moment? Since you compared the risks of smoking with that of the pill, do you know of any cases where smoking three packages of cigarettes has caused either serious illness or death? Three packages?
Dr. Kistner: Smoking three packages?
Mr. Gordon: Right.
Dr. Kistner: Obviously the answer to that question is no.
Mr. Gordon: I have here the proceedings of a conference held… at the headquarters of the American Medical Association… there are case reports, several reports where people have either died or have become seriously injured taking the pill for only 3 months, in other words, three packages of pills.
Dr. Kistner: Is there a cause and effect relationship demonstrated or proved?
Mr. Gordon: Well, it just says “Case reports: Thrombosis and embolism in patients taking the pill.”
Dr. Kistner: There is no cause and effect relationship so far as I can understand.
Mr. Gordon: They said the same thing about tobacco.
Then, there’s this exchange when Senator McIntyre tries to clear up which side effects Dr. Kistner thinks should be shared with women:
Sen. McIntyre: Well, Doctor, there is one thing that occurs to me, could you distinguish for me the difference between a side effect and a complication?
Dr. Kistner: Yes. A side effect of a drug is one that is generally accepted as occurring in some individuals as an undesirable effect other than that for which the drug is given. If one takes estrogen, one frequently becomes nauseated, estrogen “pulls in” sodium and some women don’t excrete the excess fluid and they become edematous and “blow up.” These are side effects: but if a woman takes estrogen and gets a blood clot and dies that is a complication.
Sen. McIntyre: That is more than a complication.
[Laughter]
Dr. Kistner: Well, that is the difference. I think if you asked me to explain the difference, I did.
Today, the spin is just as silly, but the humor is missing. No longer are the distortions challenged. What used to be a laughable punch line is now presented as a valid counterpoint.
Strokes Linked to Hormonal Birth Control
In 2012, the New England Journal of Medicine published the results of an extensive Danish study showing that women on birth control pills or other hormonal contraceptives are up to twice as likely to have a stroke or heart attack than non-users, but a funny thing happened to the story on its way to the press. Industry experts analyzed, mitigated, and diluted it beyond recognition.
ABC News offered the most balanced report. Their story begins with a young woman, a ‘former smoker and birth control pill user’ who suffered a stroke. However, after sharing some of the details of the study, they downplayed the results with the aid of a Spin Doctor, a gynecologist, to be exact, who said, “…pregnancy is far more likely to cause an MI or stroke than hormonal contraception.” Whenever someone dismisses a comprehensive 15-year, peer-reviewed study with a statement like this, they should be required to provide supporting evidence at least as comprehensive as the study itself. In this case, the doctor is repeating an old fallacy – a misinterpretation of statistics that has been around since the beginning of birth control.
Don’t Question Birth Control
One could argue that it is good journalism to seek out a dissenting voice – to effectively present both sides of the story. In this case, I disagree. It’s dangerous. And I have to admit, reading the responses from ‘expert’ physicians frequently brings out my snarky side. Consider the dissenting voices from these spin doctors in articles related to the same Danish study:
Huffington Post interviewed Dr. Diana Petitti, who told them:
“The amount of attention paid to these miniscule risks…detracts attention from more salient issues, like preventing unwanted pregnancy.”
Miniscule risks?! I’m not sure, but I think Dr. Petitti is saying she would rather double her daughter’s chance of having a stroke than risk her getting pregnant.
Later in the same article, Dr. Kathy Hoeger explained:
“The risk might be as much as two times greater, but when you know that the rates are 1 in 10,000, you’re just bringing it up to 2 to 4 in 10,000.”
Those numbers sound so cute, but when you think about an estimated 18 million women in the U.S. currently use hormonal birth control; we could be subjecting an additional 5,400 women per year to strokes and heart attacks.
My favorite may be Dr. Isaac Schiff, who told Boston.com:
“I would say in many ways, this is a good news story. This is a lengthy, large study that helps to confirm that the birth control pill is relatively safe, recognizing that no drug is 100 percent safe.”
He’s ecstatic that hormonal birth control only doubles the risk! He probably turned somersaults when he read that women on The Pill also have a 30% higher risk of developing Multiple Sclerosis, a 50% higher risk of developing Lupus, and could triple their chances of having Crohn’s Disease! (I will talk more about The Pill and the rise of Autoimmune Disease in future posts.)
Dissenting Voices
So, why is it dangerous to present these dissenting voices? Imagine you’re a young woman who’s just been diagnosed with a chronic disease. You begin puzzling the pieces together, and recall that your first symptoms appeared within weeks or months of starting The Pill. You take your suspicions to Google, and stumble upon an article that confirms your fears… or does it?
So, you click on another article. For example, this lupus article that tells you, “The risk was greatest during the first three months after starting “the Pill” — when there was a 2.5-fold increased risk.” You think you’re on to something, but then a prominent doctor from Johns Hopkins is quoted, “One shouldn’t oversell this. Women taking oral contraceptives need to weigh the risk/benefit of unexpected pregnancy versus a very small increase in lupus.” We can’t blame the reader for concluding her diagnosis probably didn’t have to do with The Pill after all.
The Risks versus The Optical Illusions
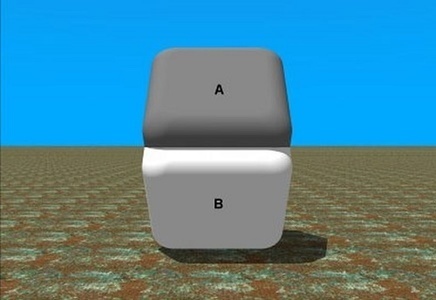
You probably saw this image floating around the internet not too long ago. It reveals a lot about how our brains process information. Our eyes take in all the curves, lighting, and shadows that define Blocks A and B, allowing our brains to analyze the difference in colors. However, when you cover the middle of the image, you discover the blocks are actually the exact same shade.
Only by covering the embellishment do you see the reality.
Media reports on epidemiological studies associated with The Pill often work like this illusion in reverse. They first give us the reality of the image – sharing some of the alarming facts or statistics from the new study. Just as the reader grows concerned that The Pill may be too dangerous, the author bevels the edges, moves the light source, and casts a different shadow.
As laypeople, we tend to assume they know more than us. They minimize the importance of the findings, and we — well, we start to look at it in an entirely different light. We walk away thinking it must not have been as bad as it originally sounded.
We can no longer afford to let reality be obscured by these tactics. Rather than having blind faith in a doctor quoted in some article, we need to consider that we could be dealing with a Spin Doctor. We’ve seen examples of some of these above, but here are five red flags that should make you think twice about the motivation of the speaker:
1) “Those Statistics Aren’t Really That Bad”
Pill proponents will attempt to re-frame numbers so that they seem insignificant. We saw a stereotypical example earlier in this article – “…you’re just bringing it up to 2 to 4 in 10,000.”
Another form of statistical acrobatics seen less frequently today is the attempt to convince us that nature is more dangerous than The Pill. You will recall the gynecologist mentioned early in this article: “…pregnancy is far more likely to cause an MI or stroke than hormonal contraception.”
I believe this method has lost some steam over the years because the mathematical contortions are so easily untangled. Consider this historical example: in his testimony at the Nelson Pill Hearings, Dr. Alan Guttmacher, President of Planned Parenthood/World Population, gave statistics suggesting pregnancy was more dangerous than The Pill (Competitive Problems in the Drug Industry, Ninety-First Congress, Second Session, Page 6565). This was a common argument at the time, but it was refuted beautifully by world-renowned neurologist, Dr. David Clark, speaking to the American Academy of Neurology,
“The woman who takes oral contraceptives is, in effect, pregnant and delivering every month. In the normal course of her life, the average American woman has 3.6 pregnancies. She is fertile for approximately 30 years. If she takes oral contraceptives, she will be pregnant and delivering 360 times in that span of time. Expressed differently, she has 90 times more chance of showing the complications of pregnancy.” (Barbara Seaman, A Doctors’ Case Against the Pill, Page 26)
2) “Old Smokers Beware”
Media reports frequently stress that the risk is greatest for women who smoke or are over 35. This is a true statement, but the slight-of-hand comes in the implied message, ‘If you’re young and don’t smoke, you have nothing to worry about,’ which couldn’t be further from the truth.
Sure, they may try to convince you that you have better odds of winning the Publisher’s Clearinghouse than developing a deadly disease, but you don’t want to be on the backside of this one, saying, “That’s what I used to think.”
3) “There is No Proof of an Association”
The US tobacco industry played the ‘Proof versus Evidence’ game masterfully for decades. In 1954, they responded to early lung cancer studies by releasing the ‘Frank Statement to Cigarette Smokers.’ In part, it said:
As recently as 1998, John Carlisle of the Tobacco Manufacturers Association said:
“There is no such thing as conclusive evidence when you are talking about such a vast subject.”
The subsequent public release of internal communications from the tobacco industry revealed exactly what they knew, and how they strategized to maintain credibility while continuing to deny the overwhelming evidence. While we can’t assume Big Pharma has been consciously playing the same game, there are signs dating back to the early days of The Pill that eerily parallel the tobacco industry’s stance:
- Complete denial of the association to cancer and strokes
- Maintain credibility by admitting danger to a ‘small number’ of consumers
- Agree to include a warning of the dangers with the product
By 1965, Morton Mintz, in the Columbia Journalism Review, expressed dismay at the ‘significant volume of reporting’ in medical journals that attempted to cast doubt on studies by using the argument that The Pill had not been proven unsafe. This was a 180-degree paradigm shift. The FDA had never been required to prove a drug unsafe. The onus was/is on the manufacturer to prove the drug safe. Clearly irritated by the ‘parroting’ in the press, Mintz wrote:
“…there was no acknowledgement that more was required – a disclosure as to specifically what weight of evidence of harm, in the eyes of the advocates, would add up to proof. Also missing was a recognition that for scientists there is no proof in the black-and-white sense, that all that can be had is evidence in one or another shade of gray.”
4) “It Could Have Been Something Else”
This is essentially a nebulous tangent of the ‘Proof vs. Evidence’ game. Despite the fact that criteria for publishing a study are extremely stringent, naysayers will attempt to cast doubt by questioning other variables that could have influenced the study. I recall one doctor actually asking, “How do we know it wasn’t the breakfast cereal the women had been eating that was causing these strokes?”
I suggest to you very few studies get published if they don’t eliminate Cocoa Puffs as a variable.
5) “The Benefits Still Outweigh the Risks”
Then there is the ubiquitous, “The benefits still outweigh the risks.” This phrase, more than any other, makes my head want to explode.
What kind of scale are they using to measure the benefits and risks? Are they looking at the isolated risk in a vacuum, and forgetting about all of the other associated risks? How do you compare a decreased chance of pregnancy with an increased risk of a deadly disease, regardless of percentages on either side, and determine that the benefits outweigh the risks?
Even if there were no other fertility control options available, I cannot grasp the idea of a healthcare professional saying, “Take this pill. It will greatly reduce the likelihood of you getting pregnant, but it doubles your risk of having a stroke…Did I mention that it will help clear your skin?”
Take Your Thumb Off the Scale
Clearly, when weighing the benefits to risks, someone has their thumb on the scale. The result is that there are many prominent physicians willing to perpetuate a pattern of denial and obfuscation anytime a new study is published. We have already seen how medical dogma can trump scientific evidence. So, whenever you read about a new study linking birth control to a deadly disease, remember that the media has run it through a decades-old filter of dogma and distortion. Isolate the Spin Doctor quotes, and take them with a grain of salt. Then, focus on the findings of the study itself. In other words, remove the embellishments and see the reality.
[atkp_product id=’48881′ template=’bestseller’][/atkp_product]
We Need Your Help
More people than ever are reading Hormones Matter, a testament to the need for independent voices in health and medicine. We are not funded and accept limited advertising. Unlike many health sites, we don’t force you to purchase a subscription. We believe health information should be open to all. If you read Hormones Matter, like it, please help support it. Contribute now.
Yes, I would like to support Hormones Matter.
This article was first published on September 13, 2016.












